Broken Endodontic File Retrieval Kit From KOMET USA
New kit provides clinicians the ability to rectify a fractured file situation.
Nickel-titanium (NiTi) files are the standard instruments for performing endodontic procedures; however, files are fragile and can break within the canal.1 Almost 80% of endodontic files that fail are mechanical NiTi files, and, in many cases, failure is because of incorrect or insufficient canal access preparation.1 A broken file can not only cause the dentist a tremendous amount of stress trying to remove it, but it poses an increased risk of post-endodontic complications to the patient.
In the past, dentists have had to rely on using large trepan burs, tweezers, sonic or ultrasonic tips, or other invasive and expensive alternatives to remove a fractured file. After 3 years of research and development, KOMET can now offer practitioners "peace of mind" and allow them the ability to rectify the situation with correct and precise re-preparation of the access using a combination of conventional rotary instruments.
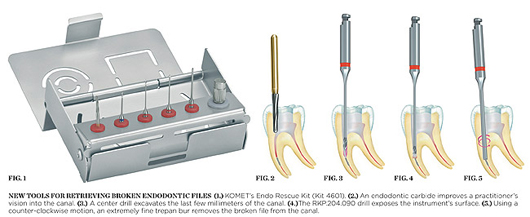
KOMET USA recently introduced the Endo Rescue Kit (Kit 4601) to the US dental market (Figure 1). Developed in conjunction with Dr. Dominique Martin of Paris, France, the Endo Rescue Kit is specifically designed for the quick and simple retrieval of a fractured rotary NiTi instrument within the canal. This easy-to-use kit, containing six instruments, is invaluable to practitioners when an emergency occurs.
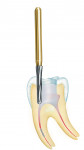
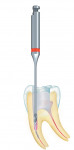
The H269GK.315.016 endodontic tungsten carbide bur, with its non-cutting tip, is designed to enlarge the pulp cavity wall, improving a practitioner's vision into the canal (Figure 2). When the canal opening is relocated and access to the fragmented head is created, two specialty instruments designed to be used in the canal allow the practitioner to simplify what was once a previously complicated procedure. The center drill (RKP.204.090) excavates the last few millimeters of the canal, providing the practitioner with enough access to the broken instrument (Figure 3). The drill then exposes the instrument's surface by drilling around the fragmented file (Figure 4).
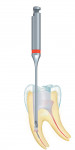
With the use of an extremely fine trepan bur (RKT.204.090), the practitioner places this instrument onto the fragment, seizing and holding it in place using residual dentin. Using a counter-clockwise motion, the broken file is then removed from the canal (Figure 5). For those practitioners who would rather not use a handpiece or whose handpiece cannot turn counter-clockwise, the kit also comes with a manual removal wrench (150.155.000) to be used with the extremely fine trepan bur or the center drill.
Conclusion
For patients, endodontic therapy is one of the most feared procedures in all of dentistry; however, with the occurrence of endodontic files fracturing, it is still not known what the complication will be by leaving these NiTi files in the body. For those dentists who refuse to leave a fractured file behind, the Endo Rescue Kit not only removes the problem immediately, but quite possibly saves both the patient and dentist future difficulties.
For more information, contact:
KOMET USA LLC
Phone: 888-566-3887
Website: https://www.komet-usa.com
E-mail: info@komet-usa.com
References
1. Spili P, Parashos P, Messer HH. The impact of instrument fracture on outcome of endodontic treatment. J Endo. 2005;31(12):845-850.
Disclaimer
The preceding material was provided by the manufacturer. The statements and opinions contained therein are solely those of the manufacturer and not of the editors, publisher, or the Editorial Board of Inside Dentistry. The preceding is not a warranty, endorsement, or approval for the aforementioned products or services or their effectiveness, quality, or safety on the part of Inside Dentistry or AEGIS Communications. The publisher disclaims responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas or products referred to in the preceding material.